
Antioxidants are substances that help prevent certain types of cell damage, especially those caused by oxidation. When certain types of oxygen molecules are allowed to travel freely in the body they cause what is known as oxidative damage which is the formation of free radicals.
Free radicals are very dangerous to the body’s tissues and have been connected to cancer and premature aging. The body uses antioxidants to prevent itself from the damage caused by oxygen.
All living organisms utilize oxygen to metabolize and use the dietary nutrients in order to produce energy for survival. Oxygen thus is a vital component for living. Oxygen meditates chemical reactions that metabolize fats, proteins, and carbohydrates to produce energy.
Dark side of oxygen
While oxygen is one of the most essential components for living, it is also a double edged sword. Oxygen is a highly reactive atom that is capable of becoming part of potentially damaging molecules commonly called “free radicals.”
Free radicals
These free radicals are capable of attacking the healthy cells of the body. This may lead to damage, disease and severe disorders. Cell damage caused by free radicals appears to be a major contributor to aging and diseases like:
- cancer
- heart disease
- decline in brain function
- decline in immune system etc.
Overall, free radicals have been implicated in the pathogenesis of at least 50 diseases.
Since free radicals contain an unpaired electron they are unstable and reach out and capture electrons from other substances in order to neutralize themselves. This initially stabilizes the free radical but generates another in the process. Soon a chain reaction begins and thousands of free radical reactions can occur within a few seconds on the primary reaction.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS)
ROS is a term which encompasses all highly reactive, oxygen-containing molecules, including free radicals. Types of ROS include the hydroxyl radical, hydrogen peroxide, the superoxide anion radical, nitric oxide radical, singlet oxygen, hypochlorite radical, and various lipid peroxides. These can react with membrane lipids, nucleic acids, proteins and enzymes, and other small molecules.
Oxidative stress
Oxidative stress means an unbalance between pro-oxidants and antioxidant mechanisms. This results in excessive oxidative metabolism. This stress can be due to several environmental factors such as exposure to pollutants, alcohol, medications, infections, poor diet, toxins, radiation etc. Oxidative damage to DNA, proteins, and other macromolecules may lead to a wide range of human diseases most notably heart disease and cancer.
Control of free radicals
Normally free radical formation is controlled naturally by various beneficial compounds known as antioxidants. When there is deficiency of these antioxidants damage due to free radicals can become cumulative and debilitating.
Antioxidants are capable of stabilizing, or deactivating, free radicals before they attack cells.
Antioxidants from food

There are several nutrients in food that contain antioxidants. Vitamin C, vitamin E, and beta carotene are among the most commonly studied dietary antioxidants.
- Vitamin C is the most important water-soluble antioxidant in extracellular fluids. Vitamin C helps to neutralize ROS in the water or aqueous phase before it can attack the lipids.
- Vitamin E is the most important lipid soluble antioxidant. It is important as the chain-breaking antioxidant within the cell membrane. It can protect the membrane fatty acids from lipid peroxidation. Vitamin C in addition is capable of regenerating vitamin E.
- Beta carotene and other carotenoids also have antioxidant properties. Carotenoids work in synergy with vitamin E.
The levels of antioxidants is evaluated by ORAC Score (oxygen radical absorption capacity) and tests the power of a plant to absorb and eliminate free radicals. These measurements were developed by the National Institute of Aging and are based on 100 grams of each food or herb.
Top 10 High Antioxidant Foods List
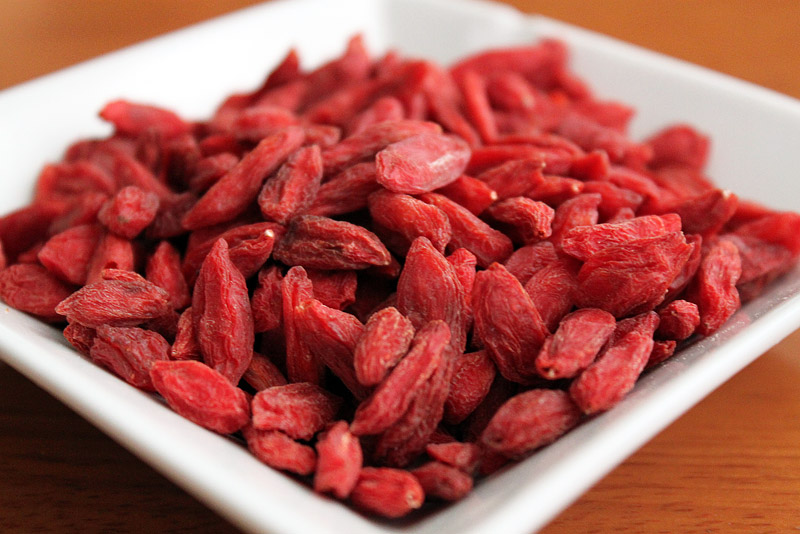

1) Goji berries
25,000 ORAC Score
2) Wild blueberries
14,000 ORAC Score
3) Dark Chocolate
21,000 ORAC Score
4) Pecans
17,000 ORAC Score
5) Artichoke
9,400 ORAC Score
6) Elderberries
14,000 ORAC Score
7) Kidney Beans
8,400 ORAC Score
8) Cranberries
9,500 ORAC Score
9) Blackberries
5,300 ORAC Score
10) Cilantro
5,100 ORAC Score
Other antioxidant rich foods include: pomegranates, strawberries, kale, red wine and wild caught salmon. Also, along with food, herbs and essential oils of plants are extremely high in antioxidants. Here is another list of the herbs and essential oils highest in antioxidants.
Top 10 Antioxidant Herbs List
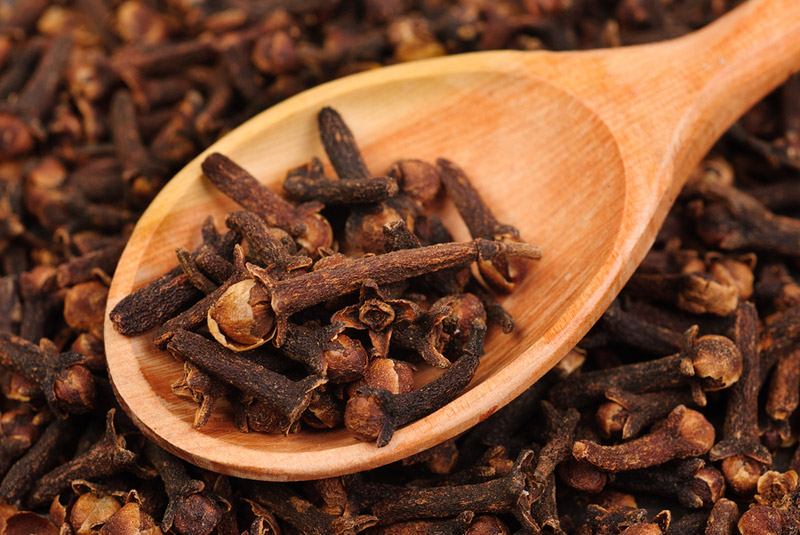

1) Clove
314,446 ORAC Score
2) Cinnamon
267,537 ORAC Score
3) Oregano
159,277 ORAC Score
4) Turmeric
102,700 ORAC Score
5) Cocoa
80,933 ORAC Score
6) Cumin
76,800 ORAC Score
7) Parsley (dried)
74,349 ORAC Score
8) Basil
67,553 ORAC Score
9) Ginger
28,811 ORAC Score
10) Thyme
27,426 ORAC Score
Other antioxidant rich herbs include garlic, cayenne pepper and green tea.
Antioxidant deficiencies
A diet low in fats may impair absorption of beta carotene and vitamin E and other fat-soluble nutrients. Fruits and vegetables are important sources of vitamin C and carotenoids. Whole grains and high quality vegetable oils are major sources of vitamin E.
Many plant-derived substances are known as “phytonutrients,” or “phytochemicals”. These also possess antioxidant properties. Phenolic compounds such as flavonoids are such chemicals. These are found in several fruits, vegetables, green tea extracts etc.
Antioxidants within the human body

Apart from diet, the body also has several antioxidant mechanisms that can protect itself from ROS mediated damage. The antioxidant enzymes – glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) are such enzymes. They require micronutrient cofactors such as selenium, iron, copper, zinc, and manganese for their activity. It has been suggested that an inadequate dietary intake of these trace minerals may also lead to low antioxidant activity.
More Is Not Better!

Some antioxidant supplements may be detrimental to your health when taken in large doses and may interact with certain medications.
- Large amounts of vitamin A supplements may cause birth defects when taken by pregnant women, and may increase your risk of cardiovascular disease and cancer.
- Taking large doses of vitamin E (over 400 International Units per day) has been associated with a possible increase in overall mortality. But, this risk doesn’t apply to a typical multivitamin supplement. The amounts of vitamins A and E included in multivitamin tablets are small in comparison.
If you’re thinking about taking larger amounts of any antioxidant supplements, you should speak with a healthcare provider first.




Leave a Reply