
The majority of mesotheliomas occur in the pleural (lung) cavity. Mesothelioma may also occur in the peritoneal (abdominal) cavity, the pericardium (heart) sac and, very rarely, the covering layer on the testicles (the tunica vaginalis). Symptoms of mesothelioma vary depending on where the cancer occurs.
Pleural mesothelioma is the most common type of mesothelioma, followed by peritoneal mesothelioma. The frequency of pericardial mesothelioma and testicular mesothelioma is quite low and the symptoms are not well understood.
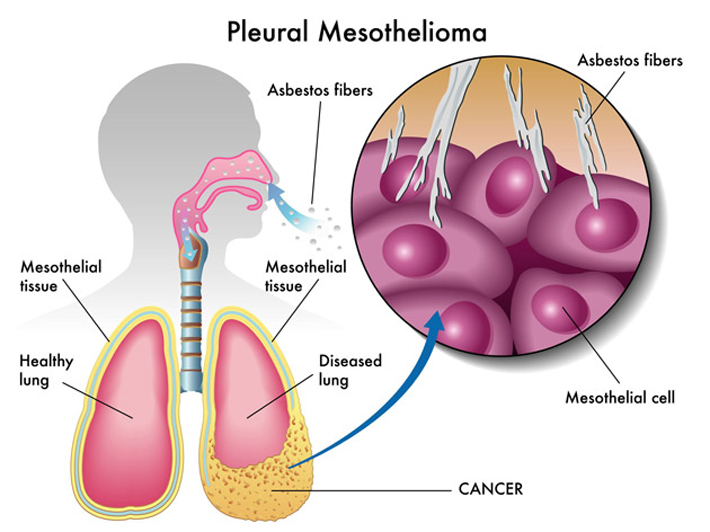
Pleural mesothelioma symptoms
The symptoms associated with pleural mesothelioma may be similar to other conditions affecting the lungs or chest. Pleural effusion, a complication of the disease, is the buildup of fluid in the chest. It may cause difficulty breathing.
Other common signs of pleural mesothelioma include:
- Pain or difficulty breathing (pleurisy)
- Chest pain
- A dry (sometimes painful) cough
- Shortness of breath
- Difficulty swallowing
- Weakness and/or fatigue
- Back pain
- Unexplained weight loss
Peritoneal mesothelioma symptoms
Tumors that develop in the membrane lining the abdominal cavity may cause pain in that area of the body (the belly).
Common peritoneal mesothelioma symptoms include:
- Abdominal pain
- Accumulation of fluid in the abdomen (swelling)
- Diarrhea, constipation or other changes in bowel habits
- Unexplained weight loss
Mesothelioma risk factors
Exposure to asbestos is a major risk factor for mesothelioma. Asbestos is a naturally occurring fibrous mineral that was found to have many useful industrial applications because of the fiber’s strength and resistance to fire and heat, as well as its low electrical conductivity.
The National Cancer Institute reports approximately three out of four cases of mesothelioma are related to a worker’s history of exposure to asbestos.
Knowing the risk factors for mesothelioma may help you take preventative measures to reduce the likelihood of developing the disease.
Lifestyle
- Smoking: Although smoking alone is not a risk factor for mesothelioma, some think that smoking in combination with asbestos exposure may increase a person’s risk of mesothelioma.
Exposure to chemicals
- Asbestos: Exposure to asbestos is a major risk factor for mesothelioma. The risk from long-term asbestos exposure does not decrease over time. Rather, it may take more than 20 years from the last exposure before cancer develops. Talk to a doctor if you or a loved one has a history of asbestos exposure.Today the risk of exposure for workers in the manufacturing industry is much less since asbestos, by and large, is no longer used in the United States. Although the use of asbestos has decreased dramatically since the late 1980s, asbestos may still be found in older buildings or products.
- SV40: Between 1955 and 1963, some polio vaccinations were infected with SV40 (simian virus 40). There is ongoing research exploring the possibility that SV40 infections may have an effect on the development of mesothelioma. Although there is no conclusive evidence, there may be an overlap in the peak age range of those who are diagnosed with mesothelioma (ages 50 to 70) and the timing of the exposure to SV40.
- Thorium dioxide: Up until the 1950s, thorium dioxide (Thorotrast) was injected into the chest or abdomen before an X-ray was taken to create contrast in the image. There may be a link between the thorium dioxide, followed by a high dose of radiation, and mesothelioma.
Please follow us on Facebook Page and enjoy our collection of recipes, crafts, fitness, health tips, gardening, DIY and more…
Source: cancercenter.com





Leave a Reply