
Many different factors can be considered when deciding which type of tomatoes to plant. You could select based on overall size, flavor, and color, suitability for slicing, growing methods, and ease of maintenance, among other things. One consideration, however, is often overlooked — tomatoes nutritional value.
If the nutritional components of tomatoes are a total mystery to you, worry not! This convenient guide will examine a few of the popular tomato varieties and help you learn about the health benefits and tomatoes nutritional value.
A Closer Look
Believe it or not, not all tomatoes are created equally. Each variety has their own nutritional content, and therefore, different benefits to offer. Here’s a closer look at a nine popular heirloom varieties and a traditional grocery store hybrid:
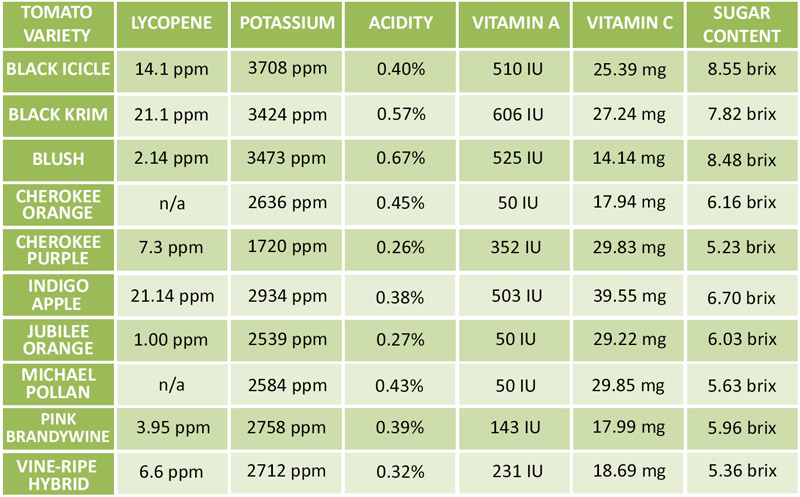
Deciphering the Color Wheel
Color can be a great indicator of the nutritional content of a specific tomato variety. The color can give you a general idea about how dense certain nutrients are in the tomatoes you’re choosing.
You may want to consider growing a few different colors to take advantage of all the nutritional benefits each color has to offer – in addition to the range of flavors you could achieve with their use. There are four main categorizations of color for tomatoes:
1. Red and Pink Tomatoes
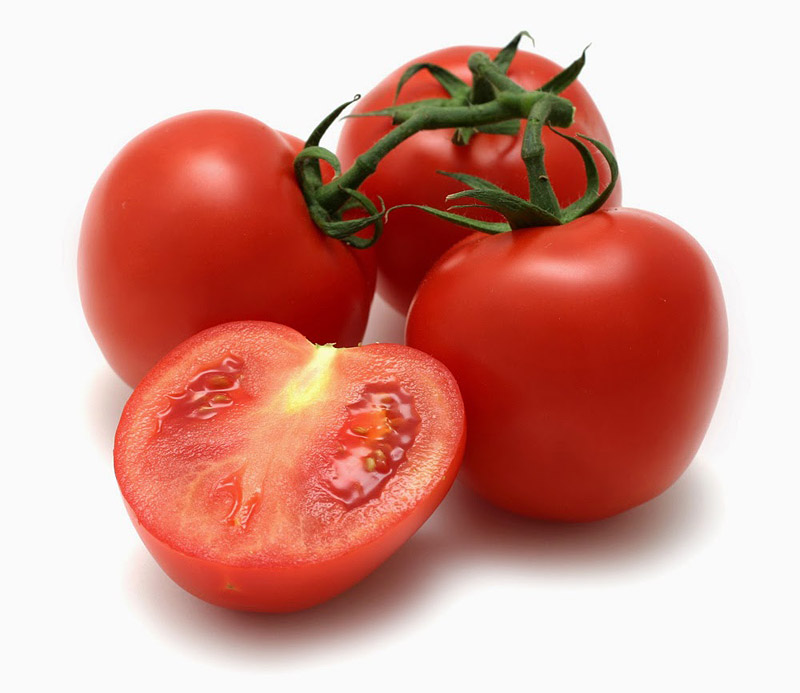

Because they’re the most common, you may be thinking that red tomatoes have the best nutritional value. It is a popular notion that a deep red color signifies that a tomato has high levels of lycopene; however, this is not always accurate. While lycopene in these tomatoes may be high, it is not as efficiently absorbed by our bodies because it is actually trans-lycopene. As for other nutrients, red and pink tomatoes have average levels when compared to some other colors.
However, you should not shy away from eating these. Red and pink tomatoes are still an excellent source of major nutrients such as lycopene, vitamin A, vitamin C, an
d potassium. These colors are great for salads and sauces, among other dishes.
2. Yellow and Orange Tomatoes
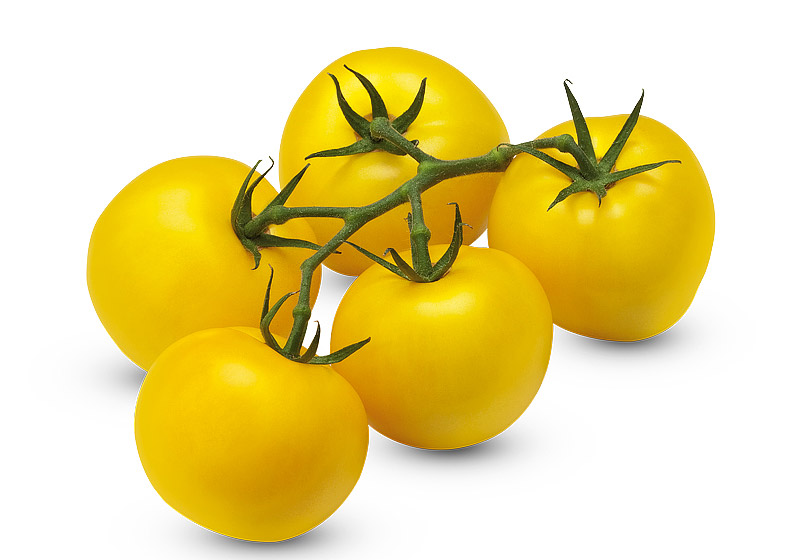

In the case of yellow and orange tomatoes, the light vs. dark color theory definitely applies. Sweeter and less acidic than their red cousins, yellow and orange tomatoes feature lower levels of the compound, lycopene. They are, however, a rich source of vitamin C and potassium – similar to other tomato colors.
Because of the signature sweet flavor, these are great when added to soups and salads.
3. Green Tomatoes
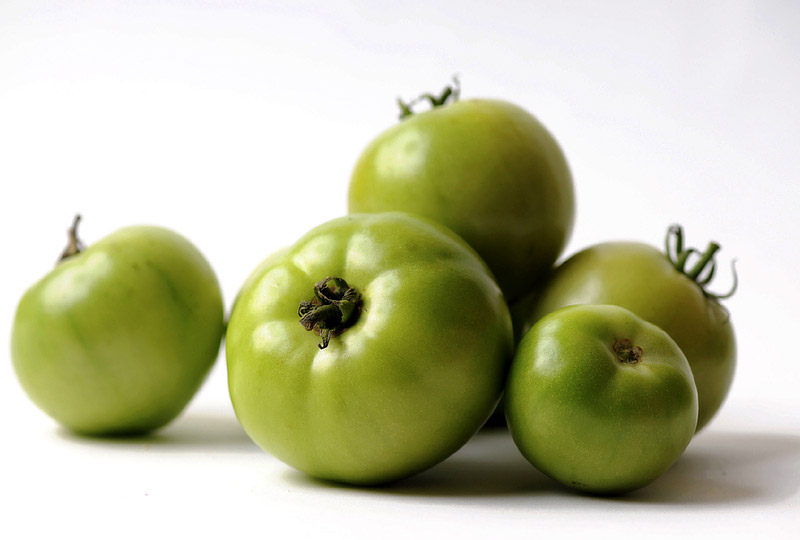

Green tomatoes are unique in terms of nutrients. When it comes to vitamin C and potassium, they have levels that are very similar to a typical red tomato. However, vitamin A is very low and lycopene is almost non-existent.
Among the other colors on this list, green tomatoes are the nutrient lightweights, but they have a lot to offer when it comes to flavor and color. They make a great addition to salsa and salads. You could also try cooking up some fried green tomatoes.
4. Black, Brown, and Purple Tomatoes
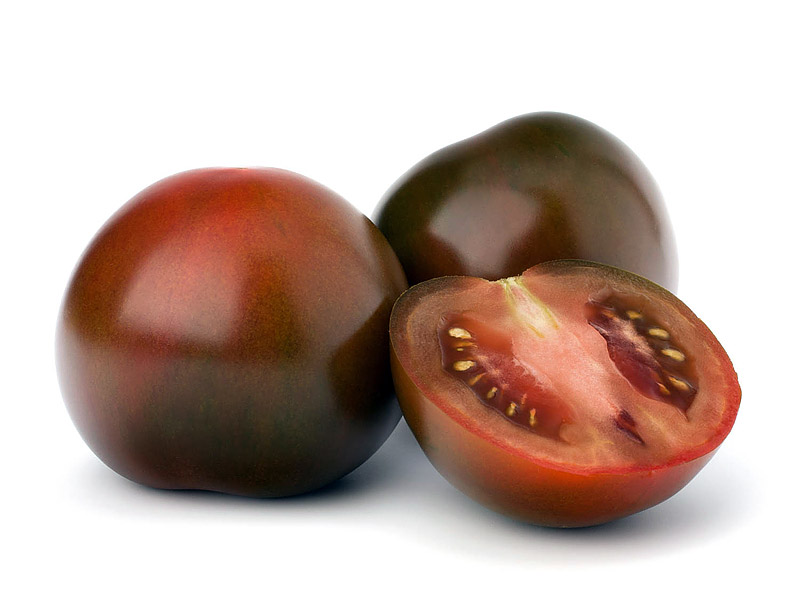

If green tomatoes are the lightweights, then purple, brown, and black tomatoes are definitely the heavyweights. The nutritional value of these dark-colored tomatoes greatly surpasses every other color variety. These colors offer high levels of lycopene, vitamin A, vitamin C, and potassium, so they are nutritionally complete in comparison to lighter colors.
Black, brown, and purple tomatoes are also packed with flavor and often have a surprisingly sweet taste. Tomatoes in these colors will create unique sauces, salads, and desserts.
Breaking Down Nutrients
As mentioned above, tomatoes are an important source of many nutrients. Further, every tomato has different densities of these nutrients.
While we all know that nutrients are important and we want to have a lot of them, do we really understand what they do for us? Take a look at what each of these vital nutrients can do for your health.
Lycopene
The most abundant compound found in tomatoes, lycopene is likely the first thing that comes to mind when you consider tomato nutrients. Lycopene is a carotenoid pigment that that is typically associated with red foods such as tomatoes and a few other fruits including watermelon – though tomatoes and tomato products are a much denser source.
For example, watermelon, on average, has only two-thirds the amount of lycopene that tomatoes do in a serving. Lycopene is also a powerful flavonoid antioxidant, which is known for having many beneficial health effects.
Expert tip: While raw tomatoes have many benefits, cooking them releases the full health nutritional power of lycopene.
Health Benefits:
- Can reduce risk of skin cancer and sunburn by protecting skin from UV rays
- Can protect against the development of breast cancer and prostate cancer
- Effective at lowering LDL cholesterol
- Improves heart health, lowering the risk of heart attacks
- Protects bone tissue, helping to prevent the onset of osteoporosis
Potassium
Potassium is an essential mineral that can be found in most foods to some degree – but tomatoes have an abundant source of it. This mineral is a necessary element of your overall health and maintaining normal body functions.
Many tomato varieties are considered a high-potassium food. A medium red tomato offers more potassium than other powerhouse foods such as carrots, brussel sprouts, avocado, and squash.
Health Benefits:
- Supports the function of tissues and organs
- Helps you maintain fluid balance
- Reduces risk of stroke
- Keeps the digestive system functioning normally
- Regulates blood pressure and promotes heart and kidney health
Vitamin A

When processed, the carotenoid pigment beta-carotene is converted into Vitamin A, which is an essential nutrient. Like lycopene, Vitamin A is another flavonoid antioxidant that has many advantages for our health.
While the vitamin A levels in tomatoes pale in comparison to beta-carotene-packed carrots – which offer 113% of our daily values – tomatoes are still a great source for this beneficial nutrient.
Health Benefits:
- Protects against lung cancer and cancers of the oral cavity
- Promotes healthy mucus membranes, skin, and bones
- Improves general eye health and protects from age-related vision problems
- Boosts the immune system
Vitamin C
Vitamin C is an essential nutrient for every diet and works as a powerful antioxidant. While tomatoes may not be the first fruit that comes to mind when you think about vitamin C, they are actually an excellent source of the nutrient, with a medium red tomato providing up to 40% of daily values.
Some tomatoes actually have levels of vitamin C that are comparable to oranges. However, it should be noted that, unlike lycopene, much of the vitamin C could be lost in the cooking process.
Health Benefits:
- Boosts the immune system
- Provides resistance against infections and harmful free radicals




Leave a Reply